
Atomical "concerned with atoms," also "very minute," is from 1640s. Wells ("The World Set Free"), who thought of it as a bomb "that would continue to explode indefinitely." When you can drop just one atomic bomb and wipe out Paris or Berlin, war will have become monstrous and impossible. Ītomic bomb is first recorded 1914 in writings of H.G. It was in March, 1903, that Curie and Laborde announced the heat-emitting power of radium. It is, also, as we shall show, a date to which, in all probability, the men of the future will often refer as the veritable beginning of the larger powers and energies that they will control. March, 1903, was an historic date for chemistry. Atomic number is attested from 1821 atomic mass is from 1848.Ītomic energy is recorded by 1906 in the modern sense (as intra-atomic energy from 1903). 1999‑2023 - All Rights Reserved."pertaining to atoms," 1670s as a philosophical term (see atomistic) scientific sense dates from 1811, from atom + -ic. Retrieved from Ĭopyright © Israel Science and Technology Directory. "Sortable list of elements of the Periodic Table". The story behind the discovery that elements are born in stars.Atomic Weights of the Elements (From IUPAC).Multilingual Dictionary and Etymology of the Periodic Table Elements.Atomic Reference Data for Electronic Structure Calculations.List of Periodic Table Elements in Hebrew.Other resources related to the Periodic Table For these elements, the weight value represents the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element.Įlectron configuration: See next page for explanation of electron configuration of atoms. The elements marked with an asterisk have no stable nuclides. The values shown here are based on the IUPAC Commission determinations ( Pure Appl. For relative abundances of isotopes in nature, see reference on Atomic Weights and Isotopic Compositions.Ītomic weight: Atomic weight values represent weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The abundance of each isotope depends on the source of materials. For example, the two common isotopes of carbon, 12C and 13C, have 6 and 7 neutrons, respectively. But many elements exist in different isotopes. It is the positively charged particle that, together with the electrically neutral particles called neutrons, make up the nucleus of an atom. Actually, the atomic mass unit is currently defined as assigning a mass of exactly 12 amu to a carbon-12 atom. Elements have more than one isotope with varying numbers of neutrons. proton, one of the three basic subatomic particlesalong with neutrons and electronsthat make up atoms, the basic building blocks of all matter and chemistry. The isotope of an element is defined by the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Isotope: Atoms of the same element with the same atomic number, but a different number of neutrons. Thus, each proton and neutron has a mass of about 1 amu. This isotope of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Atomic mass is measured in Atomic Mass Units (amu), which are scaled relative to carbon, 12C, that is taken as a standard element with an atomic mass of 12. Each element is uniquely defined by its atomic number.Ītomic mass: The mass of an atom is primarily determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Boiling pointĪtomic number: The number of protons in an atom. For the Year of Discovery of elements see the list with the English and Hebrew names.For these elements, the weight value shown represents the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element. The elements marked with an asterisk (in the 2nd column) have no stable nuclides.The protons and neutrons form the atom’s central nucleus.
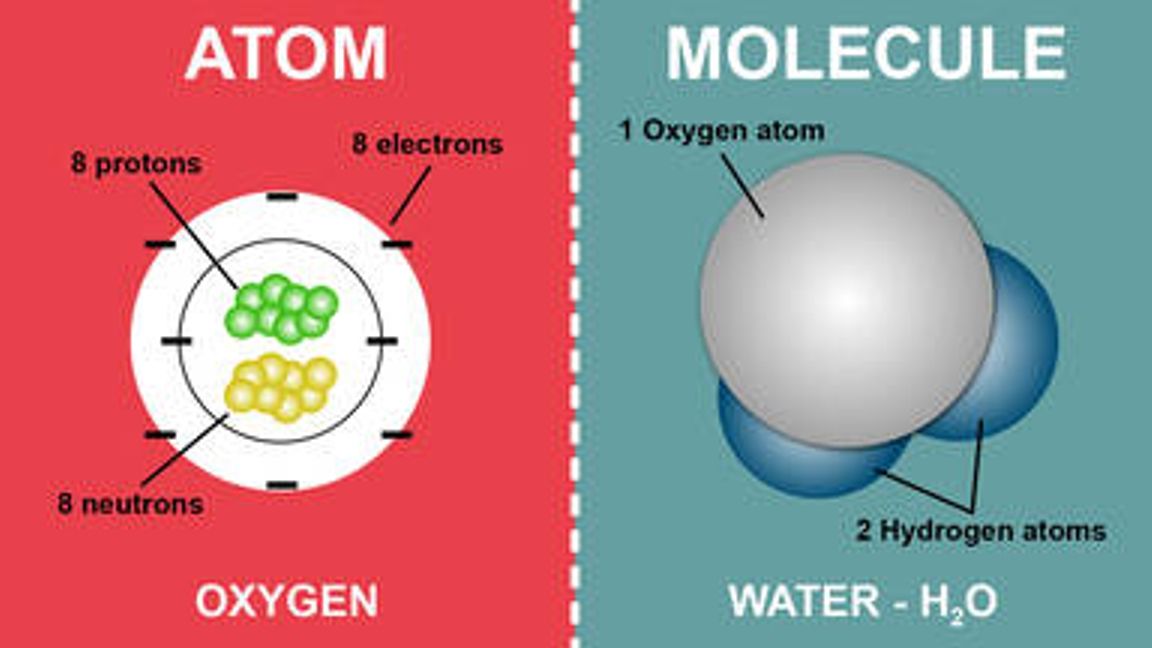
The rest consists of three basic types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Atoms can combine with other atoms to form molecules but cannot be divided into smaller parts by ordinary chemical processes.
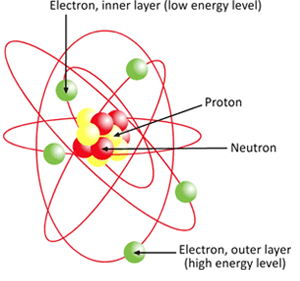
Lanthanoids and Actinoids are numbered as 101 and 102 to separate them in sorting by group. atom, the basic building block of all matter and chemistry.

An atom is composed of sub-atomic particles and these cannot be made or destroyed. In a sorted list, these elements are shown before other elements that have boiling points >0☌. An atom is defined as the smallest unit that retains the properties of an element.

The density of elements with boiling points below 0☌ is given in g/l.List of Periodic Table elements sorted by → Atomic number No.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
